
Securing Access: Understanding Authentication Techniques

Securing Access: Understanding Authentication Techniques
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Registration
- Using Advanced Installer
- GUI
- Working with Projects
- Installer Project
* Product Information
* Resources
* Package Definition
* Requirements
* User Interface
* System Changes
* Server
* Internet Information Services Page”)
* IIS Server
* Global Settings
* Website Settings
* Physical Path Credentials Dialog
* Web Site Bindings/SSL Settings
* Virtual Directory Settings
* ASP.NET Settings
* Access Flags
* Authentication
* Default Document
* Website Performance
* FTP Access
* FastCGI Settings
* ISAPI Filters
* MIME Types
* Application Mapping
* HTTP Response Headers
* Machine Key
* HTTP Error Handling
* .NET Error Handling
* Custom Properties
* Application Pools
* Web Deploy Packages
* Legacy Options
* IIS Browse
* ODBC
* SQL Databases
* SharePoint Page
* Silverlight Page
* Custom Behavior - Patch Project
- Merge Module Project
- Updates Configuration Project
- Windows Store App Project
- Modification Package Project
- Optional Package Project
- Windows Mobile CAB Projects
- Visual Studio Extension Project
- Software Installer Wizards - Advanced Installer
- Visual Studio integration
- Alternative to AdminStudio/Wise
- Replace Wise
- Migrating from Visual Studio Installer
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Shell Integration
- Command Line
- Advanced Installer PowerShell Automation Interfaces
- Features and Functionality
- Tutorials
- Samples
- How-tos
- FAQs
- Windows Installer
- Deployment Technologies
- IT Pro
- MSIX
- Video Tutorials
- Advanced Installer Blog
- Table of Contents
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
Authentication
IIS Authentication requires users to provide a valid Microsoft Windows user-account name and password before they access any information on your server. Authentication, like many IIS features, can be set at the web site or virtual directory level.
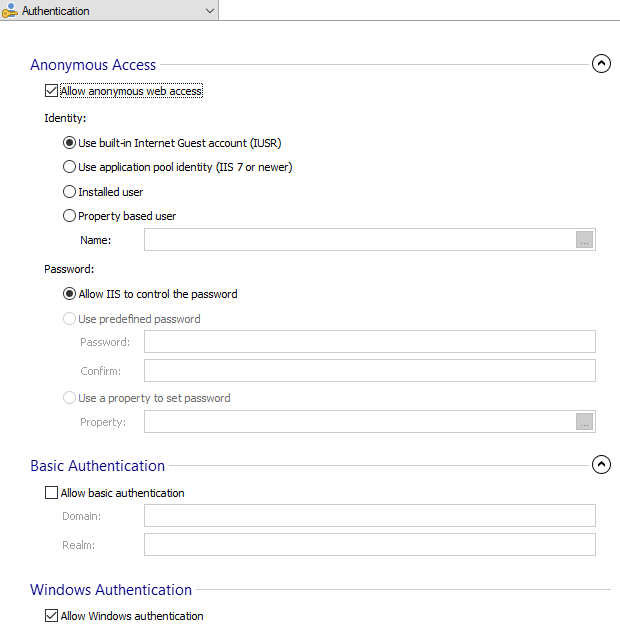
Anonymous Access
Anonymous authentication gives users access to the public areas of your Web Site or Virtual Directory without prompting them for a user name or password.
Allow anonymous web access
When a user attempts to connect to your public Web Site or Virtual Directory, your Web server assigns the connection to a Windows user account. By default, the IUSR_computername account is included in the Windows user group Guests. This group has security restrictions, imposed by NTFS permissions, that designate the level of access and the type of content available to public users.
Starting with IIS 7, the built-in Internet Guest Account was changed to IUSR.
If you have multiple sites on your server or if you have areas of your site that require different access privileges, you can create multiple anonymous accounts, one for each Web Site or Virtual Directory. By giving these accounts different access permissions or by assigning these accounts to different Windows user groups, you can grant users anonymous access to different areas of your public Web content.
Identity
Use built-in Internet Guest Account (IUSR) - Select this option if you want to assign the default IIS user account to handle incoming web content access.
Use application pool identity (IIS 7 or newer) - Select this option to enable IIS processes to run using the account that is configured for the associated application pool .
Installed user - You can configure an installed User Account to handle incoming web content access.
Property based user - The user name can be set through a Windows Installer property.
Password
Allow IIS to control the password - This mode indicates whether IIS should handle the user password for anonymous users attempting to access resources.
Use predefined password - This mode is used to set the password when the user account name is set with a property; otherwise the password used is the one configured in the Users and Groups section.
Use a property to set password - The password can also be set through a Windows Installer property.
Basic Authentication
Basic authentication requires that users provide a valid user name and password to access content.
Allow basic authentication
This authentication method does not require a specific browser, and all major browsers support it. Basic authentication also works across firewalls and proxy servers. For these reasons, it is a good choice when you want to restrict access to some, but not all, content on a server.
The disadvantage of Basic authentication is that it transmits unencrypted base64-encoded passwords across the network. You should use Basic authentication only when you know that the connection between the client and the server is secure. The connection should be established either over a dedicated line or by using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption and Transport Layer Security (TLS).
You must disable Anonymous authentication if you want to use Basic authentication. The first request that all browsers send to a Web server is for anonymous access to server content. If you do not disable Anonymous authentication, users can access all the content on your server anonymously, including restricted content.
Domain
Type a default domain or leave it blank. Users who do not provide a domain when they log on to your site are authenticated against this domain.
Realm
Type a realm or leave it blank. In general, you can use the same value for the realm name as you used for the default domain.
If you enter the default domain name in the Realm text box, your internal Microsoft Windows domain name may be exposed to external users during the user name and password challenge.
Windows Authentication
Integrated Windows authentication is a secure form of authentication because the user name and password are hashed before being sent across the network.
Allow Windows authentication
When you enable Integrated Windows authentication, the user’s browser proves its knowledge of the password through a cryptographic exchange with your Web server, involving hashing. Integrated Windows authentication uses Kerberos authentication and NTLM authentication.
Unlike Basic authentication, Integrated Windows authentication does not initially prompt for a user name and password. The current Windows user information that is on the client is used for Integrated Windows authentication. If the authentication exchange initially fails to authorize the user, Internet Explorer prompts the user for a Windows account user name and password, which it processes using Integrated Windows authentication.
Did you find this page useful?
Please give it a rating:
Thanks!
Report a problem on this page
Information is incorrect or missing
Information is unclear or confusing
Something else
Can you tell us what’s wrong?
Send message
Also read:
- [New] 2024 Approved InstaCrafts Seamless Video Assemblies on Android/iOS
- AOMEI Backupperをコマンドプロンプトで利用したPCのバックアップ手順
- Best VFX Tools of 2024: The Ultimate Guide for Film Production
- Comprehensive Steps to Moving Your Operating System From HDD to Solid State Drive
- How to Carry Over Your Previous iPhone's Voicemail Setup When Switching to the Latest iPhone Models (iPhone 14 and 15)
- How to Transfer Big iTunes Videos to Your Computer Successfully
- In 2024, Optimal Drone Cameras Film & Snapshot Heroes #10
- In 2024, Top 5 from ZTE Blade A73 5G to iPhone Contacts Transfer Apps and Software | Dr.fone
- Resolver El Error De Falta De Espacio en Su Disco Duro Para Windows 11, 8 O 7
- Solutions Rapides Pour Récupérer L'espace Disque Sur Une Clé USB Avec Windows 10/11
- Top 5 from Honor Magic 5 Pro to iPhone Contacts Transfer Apps and Software | Dr.fone
- Top Reasons to Steer Clear of ChatGPT Applications in the Apple Macintosh Application Catalog
- Unlock Artistic Methods in FB Video Ad Production
- Title: Securing Access: Understanding Authentication Techniques
- Author: Stephen
- Created at : 2024-10-12 05:41:12
- Updated at : 2024-10-16 21:22:18
- Link: https://fox-place.techidaily.com/securing-access-understanding-authentication-techniques/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.